 |
Figure 1. Photo of a three-dimensional porous gold film. (A) Photographs of gold films on FTO; (B) Scanning electron micrographs of gold films.
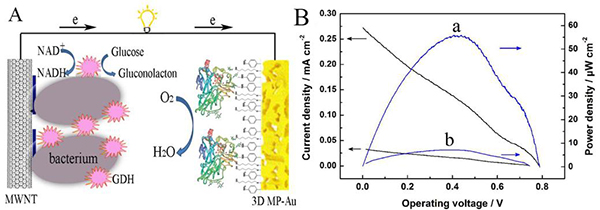
Figure 2. (A) Schematic diagram of a biofuel cell. The bioanode is a bacterial-GDH/polymethylene blue/multi-walled carbon nanotube/glassy carbon electrode. The biocathode is a laccase-immobilized three-dimensional porous gold membrane. (B) The curve of battery power density versus output voltage. a, the biocathode is a laccase-immobilized three-dimensional porous gold film; b, the biocathode is a disk gold electrode.
A biofuel cell is a special type of fuel cell that uses enzymes or electrogenic microorganisms as biocatalysts to electrochemically convert the chemical energy in biomass fuels into electrical energy.
Biofuel cells have mild reaction conditions, cheap raw material sources, and good biocompatibility. Therefore, they have good application prospects. Recently, researchers of the Biosensing Technology Team of the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences have made series of research progresses on biofuel cells based on bacterial surface display of enzymes, and developed new types of batteries with higher energy output and stability. Implantable on-body power supplies and portable power supplies are widely used.
The team, Dr. Hou Chuantao, used a biotemplate method to prepare a gold film with a three-dimensional porous structure on a fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) conductive glass (Fig. 1), and used it as an electrode to covalently immobilize laccase to make a biological cathode. The three-dimensional porous gold film can significantly increase the immobilization efficiency of the enzyme and achieve direct electron transfer, and the initial potential for catalytic reduction of oxygen is as high as 0.62 V (vs. saturated calomel electrode).
Bioanodes use bacterial surface-displayed glucose dehydrogenase mutants (bacteria-GDH). The assembled single cell battery has an open circuit potential of up to 0.80V and a maximum power density of 55.8 μW cm-2. Not only that, the battery still maintains a maximum power density of 84% after 55 hours of continuous operation, exhibiting high stability. This study basically solved the problem of low stability and high cost of enzymes in enzyme-based fuel cell research. The relevant results were published online in Analytical Chemistry (C. Hou, et al., Analytical Chemistry 2014, Article ASAP, DOI: 10.1021/ Ac501203n).
The researchers also published research results on a bacteria-free display of bacterial-XDH as a bioanode for a diaphragmless biofuel cell. The system has an open circuit potential of up to 0.58 V, a maximum output power density of 63 μWcm-2, and a maximum energy output of 85% or more after 12 hours of continuous operation. Compared to the same enzyme purified XDH-modified anode, the power density increased by 60% (L. Xia, et al, Biosensors & Bioelectronics 2013, 44, 160). In addition, the research team also constructed a starch-fueled sequential enzyme biofuel cell, and related results were also published in Biosensors and Bioelectronics. (Q. Lang, et al., Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2014, 51, 158-163).
The above study was completed by the researcher Liu Aijun and obtained funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
supplement for Zinc, anti-itch for cosmetic, For industrial usage, Zinc acetaet can be used in wood preservation, manufacturing other zinc salts, polymers, manufacture of ethyl Acetate, as a dye mordant, and analytical reagent.
Zinc Acetate,Zinc Acetate Dihydrate Pharmaceutical Grade,Molecular Formula is Zn(CH3CO2)2·2H2O,INS Code is E650
Jiangsu Kolod Food Ingredients Co., Ltd. , https://www.kolodchem.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)